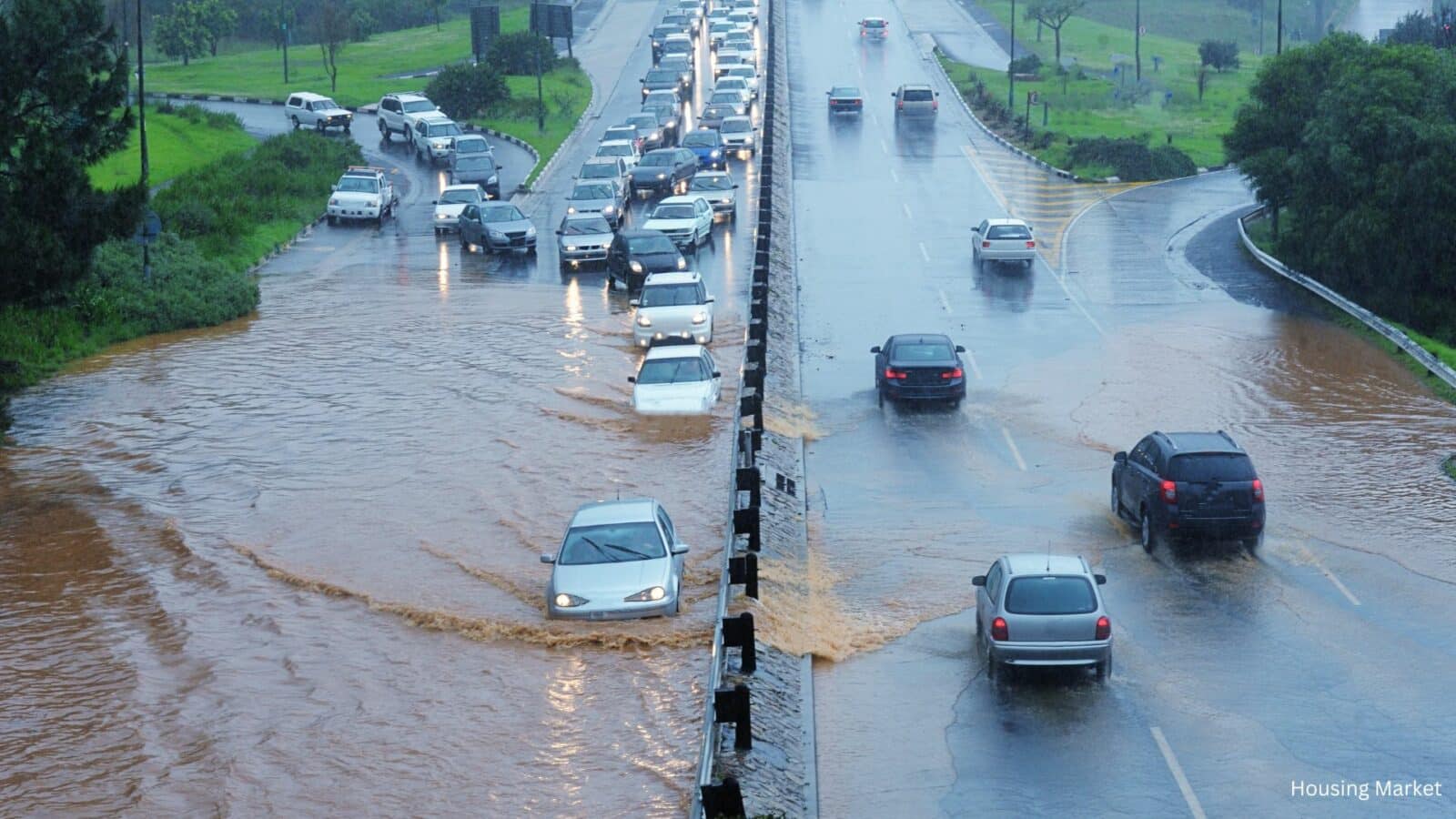
Migration to high-risk areas, such as those prone to wildfires, floods, and extreme heat, has become a significant trend in recent years. Despite the increased awareness of climate risks, many people are choosing to move to these areas for various reasons, including affordable housing, job opportunities, and lifestyle preferences. This article explores the driving factors behind this migration and the implications for residents and policymakers alike.
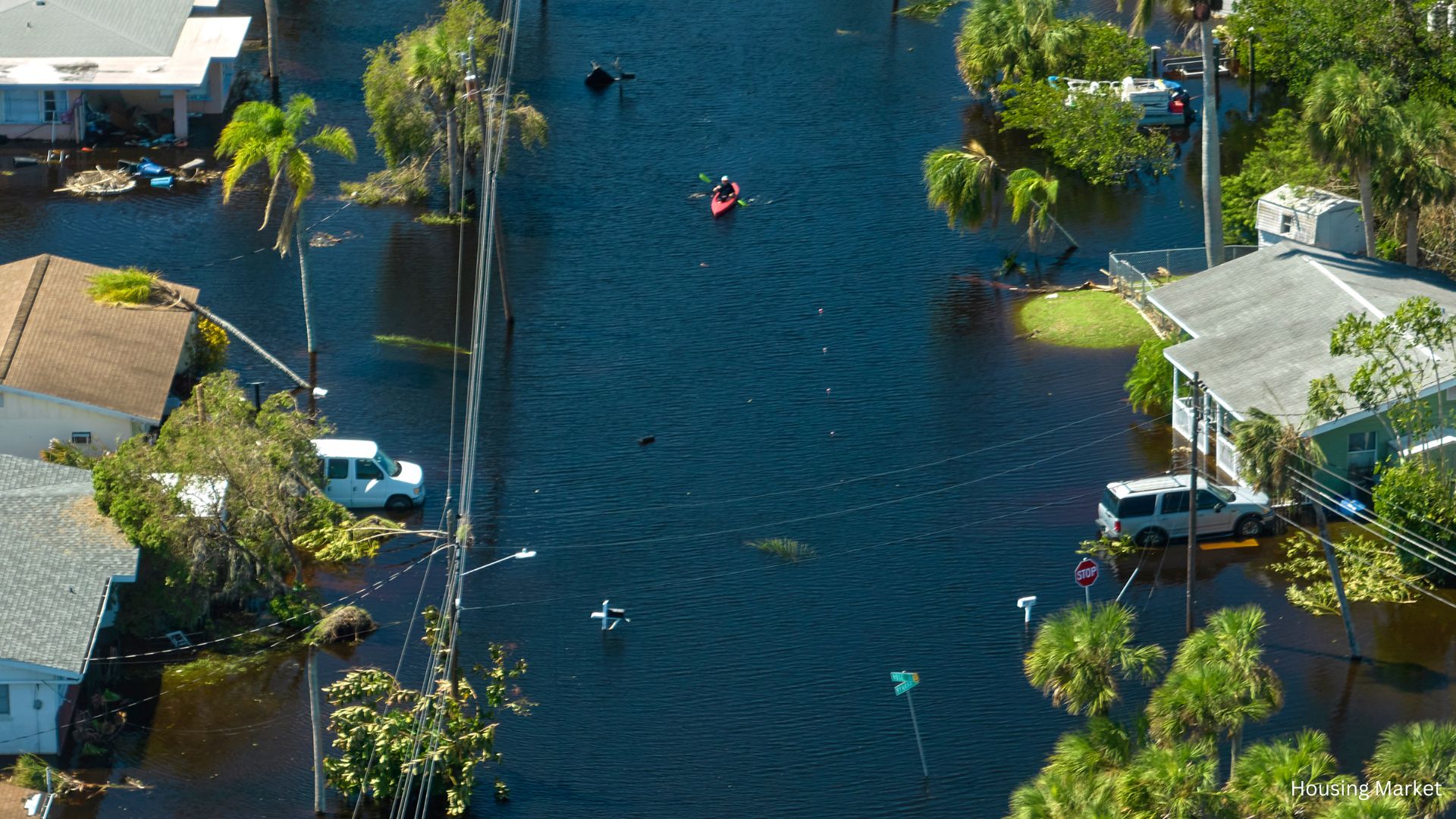

Why People Are Moving to High-Risk Areas
The phenomenon of migration to high-risk areas is largely driven by economic and lifestyle factors. States like Texas and Florida, known for their high fire and flood risks, have experienced substantial population growth. This growth is attributed to the availability of affordable housing, lower taxes, and a strong job market.
- Affordable Housing: Many high-risk areas offer more affordable housing options compared to low-risk regions. This is a major draw for individuals and families looking to purchase a home without breaking the bank.
- Lower Taxes: States like Texas and Florida are known for their lower tax rates, which attract people looking to reduce their cost of living.
- Job Opportunities: Rapid development and economic expansion in these areas provide numerous job opportunities, enticing people to relocate despite the risks.
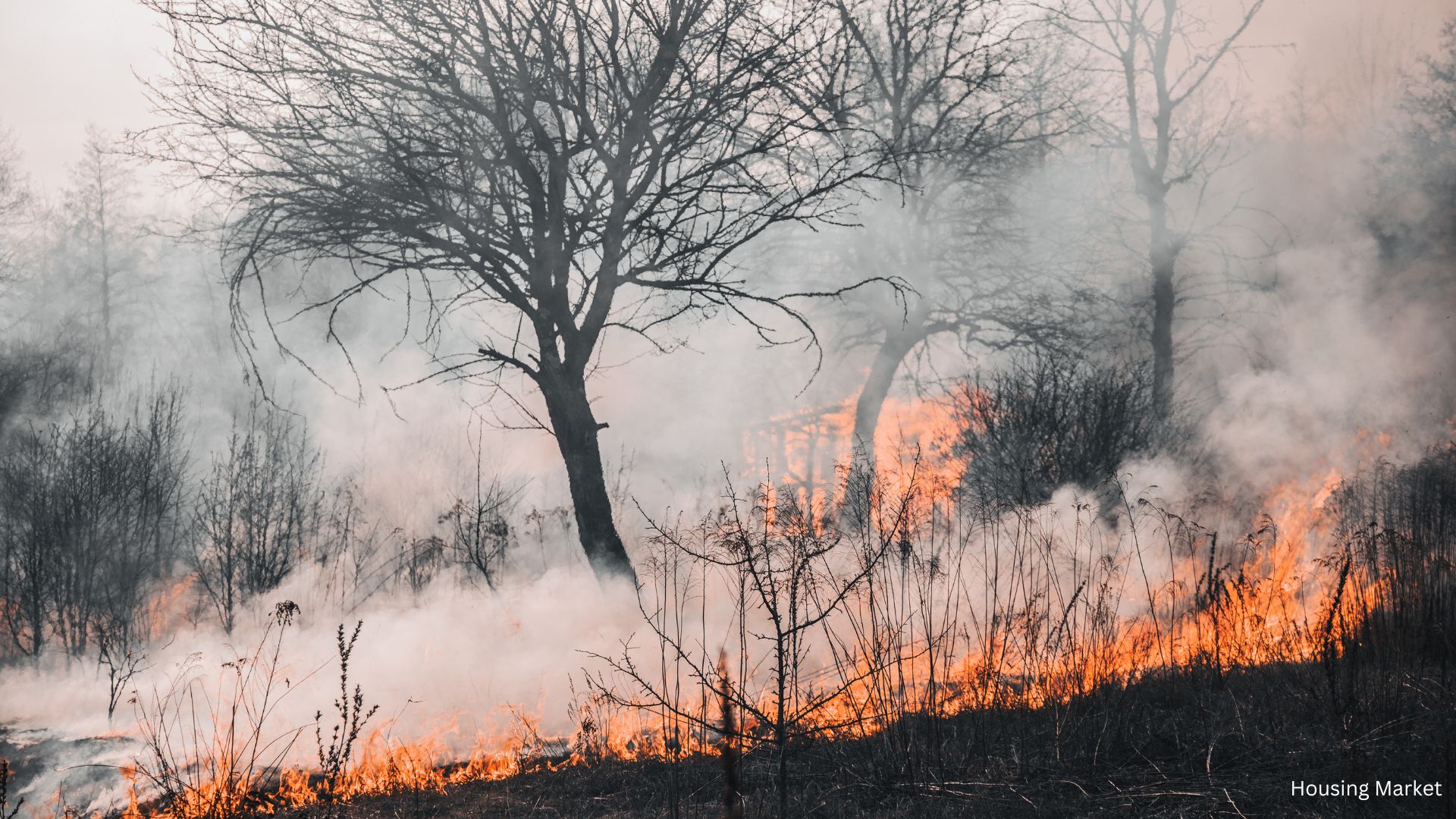

The Impact of Climate Change on Migration Patterns
While economic factors play a significant role in migration to high-risk areas, climate change is an underlying force that cannot be ignored. As climate risks increase, so does the potential for devastating impacts on these communities.
- Wildfires: In states like California and Texas, wildfires have become more frequent and intense, posing a significant threat to homes and infrastructure.
- Flooding: Coastal areas in Florida and Texas are particularly vulnerable to flooding, exacerbated by rising sea levels and severe weather events.
- Extreme Heat: Regions with high heat risks, such as Arizona, are seeing population growth despite the challenges posed by extreme temperatures.

Migration Trends in High-Risk Areas
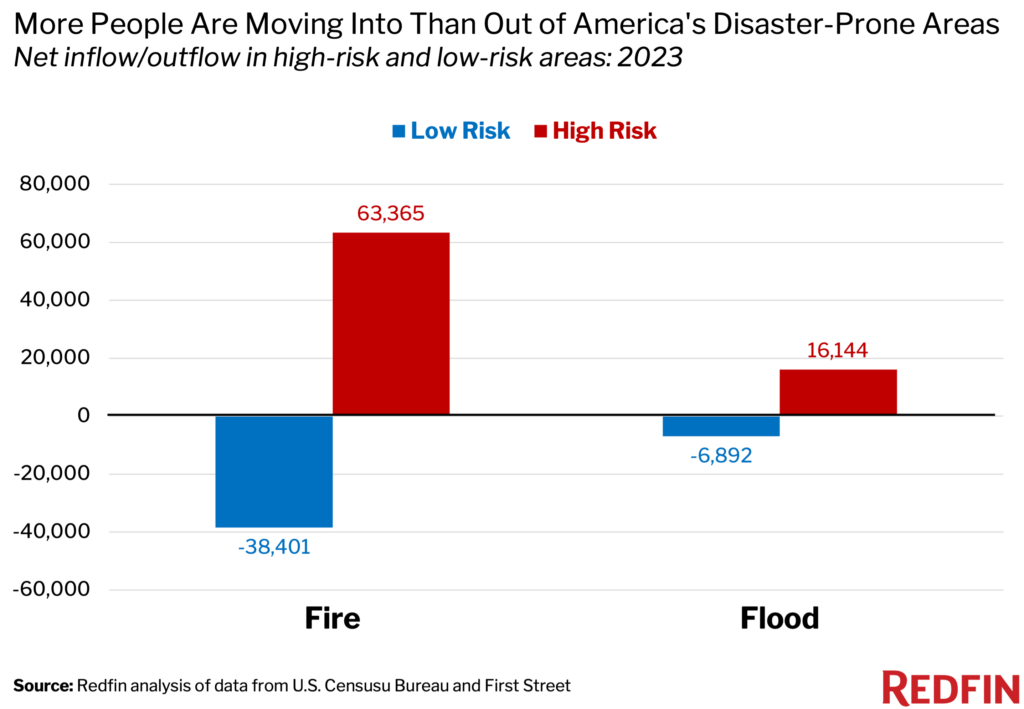
According to a recent Redfin analysis, migration to high-risk areas has shown surprising trends. In 2023, America’s high-fire-risk counties saw a net inflow of 63,365 people, with Texas being a major destination. Meanwhile, high-flood-risk counties experienced a net inflow of 16,144 people, driven by migration to Florida.
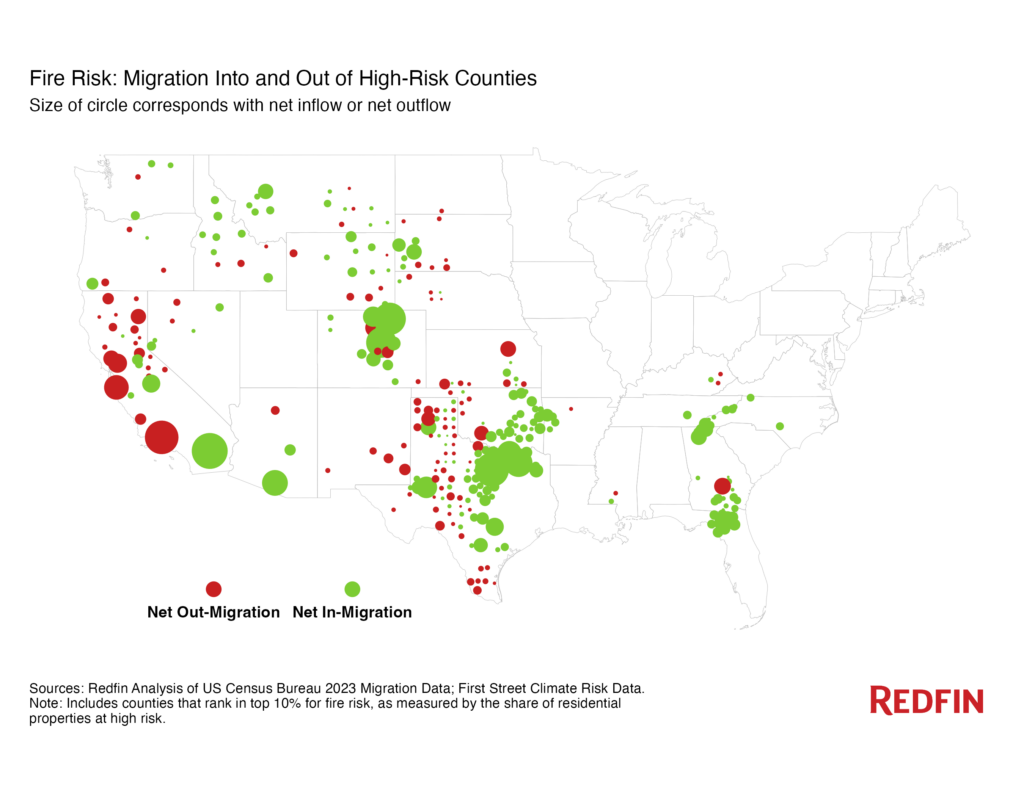
Interestingly, some regions are witnessing a reversal in these trends. For example, California, known for its high fire risk, saw more people leaving than moving in last year. This suggests a growing awareness and responsiveness to climate risks among residents.
The Future of Migration to High-Risk Areas
As climate risks continue to evolve, the future of migration to high-risk areas remains uncertain. Policymakers and residents must balance the economic benefits of living in these regions with the potential dangers posed by climate change.
Home Insurance Challenges: One of the significant challenges faced by residents in high-risk areas is the rising cost of home insurance. Insurers are adjusting their policies and premiums to account for the increased risk of natural disasters, making it more expensive for homeowners to protect their properties.
Building Resilience: As the trend of migration to high-risk areas continues, there is a growing need for resilience-building measures. This includes implementing stricter building codes, investing in infrastructure improvements, and enhancing emergency response capabilities.
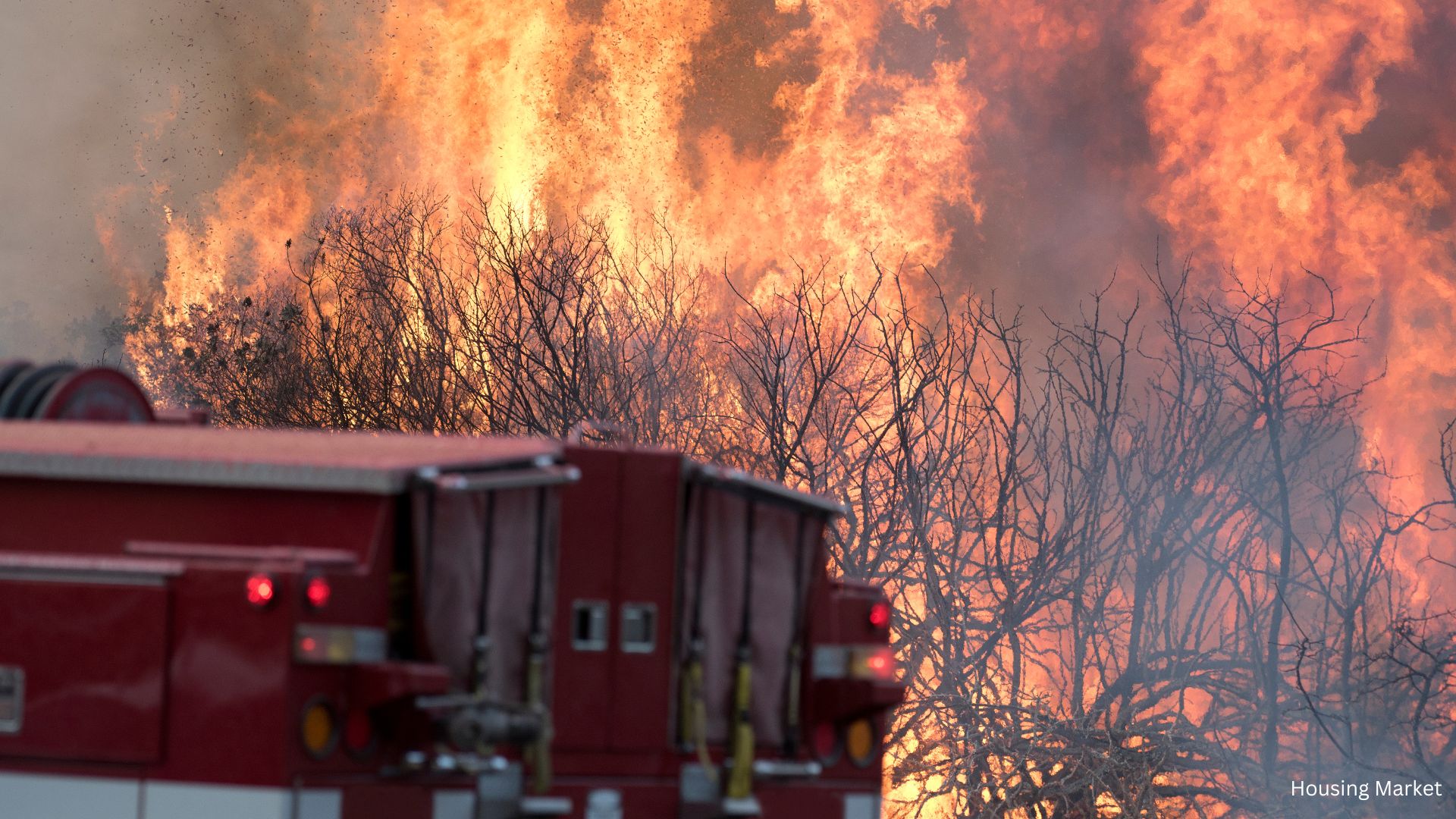

Migration to high-risk areas is a complex issue influenced by economic, social, and environmental factors. While the allure of affordable housing and job opportunities is strong, the risks posed by climate change cannot be ignored. As people continue to move to these regions, it is crucial for policymakers, communities, and individuals to work together to mitigate risks and build resilient communities.
Related posts:
 Affordable Rental Provider Repays $710K to Arlington County
Affordable Rental Provider Repays $710K to Arlington County
 Northern Virginia Housing Market – March 2023
Northern Virginia Housing Market – March 2023
 UVM-Burlington Student Housing Agreement: A Collaborative Solution to Campus Housing Challenges
UVM-Burlington Student Housing Agreement: A Collaborative Solution to Campus Housing Challenges
 Understanding Redlining in Las Vegas and Its Impact on the Westside
Understanding Redlining in Las Vegas and Its Impact on the Westside
 Boomers Staying Put and Not Leaving Their Large Homes. Why?
Boomers Staying Put and Not Leaving Their Large Homes. Why?



