Home insurance rates can vary significantly from state to state due to several factors such as climate risks, state regulations, and local economic conditions. This article explores how and why home insurance rates differ across the United States.
Home Insurance Rate Overview
The home insurance rate is a critical consideration for homeowners. In 2024, the average home insurance premium in the U.S. is approximately $2,601 annually, but this can range widely depending on the state.

Factors Influencing Home Insurance Rates
-
Climate and Weather Risks
- States prone to natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires tend to have higher insurance rates. For example, Florida and Oklahoma have some of the highest premiums due to frequent severe weather events.
- An analysis by The New York Times highlighted that areas like Enid, Oklahoma, have high home insurance costs relative to home values despite not being the most vulnerable to damaging weather. This reveals a distortion in America’s system of pricing home insurance, driven by climate change and other factors.
-
State Regulations
- State-specific regulations play a significant role in determining home insurance rates. States with stringent regulatory oversight, like California, often have lower premiums compared to states with less regulation. In Oklahoma, where regulation is minimal, premiums can be as high as $5,858 annually.
- The New York Times article explains that higher premiums are often charged in states where regulators apply less scrutiny to rate increase requests. Conversely, states with tight control over insurance rates tend to have lower premiums.
-
Economic Factors
- The cost of living, including labor and construction materials, affects insurance rates. Higher rebuild costs due to inflation and supply chain issues have increased premiums nationwide.
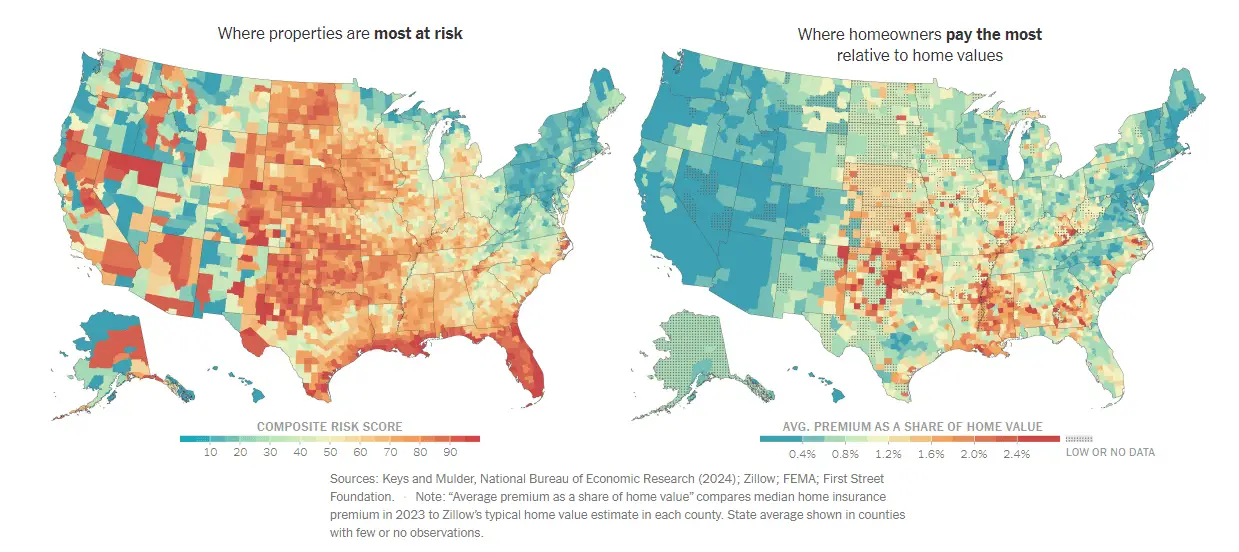
State-by-State Comparison
Highest Home Insurance Rates
Oklahoma: $5,858 annually
- Severe Weather Risks: Oklahoma is highly prone to tornadoes, hailstorms, and other severe weather events, making it one of the most hazardous states for homeowners. The frequent occurrence of these natural disasters significantly drives up insurance costs.
- Regulatory Environment: Oklahoma has relatively lax regulations regarding insurance rate increases, allowing insurers to raise rates with minimal oversight. This lack of stringent regulation contributes to higher premiums.
Kansas: $4,843 annually
- Tornado Alley: Similar to Oklahoma, Kansas is part of Tornado Alley and experiences frequent tornadoes and severe storms. These natural hazards lead to higher claims and thus higher insurance rates.
- High Cost of Reinsurance: Insurance companies in Kansas face high reinsurance costs due to the significant risk of natural disasters. These costs are passed on to homeowners through higher premiums.
Nebraska: $4,800 annually
- Severe Storms: Nebraska also falls within Tornado Alley and is susceptible to tornadoes, hailstorms, and severe thunderstorms. These weather conditions increase the risk for insurers and drive up home insurance rates.
- Low Population Density: Nebraska’s rural nature means there are fewer homes to spread the risk among, leading to higher premiums for those insured.
Florida: $4,419 annually
- Hurricane Risk: Florida faces a high risk of hurricanes and tropical storms, which cause extensive damage and lead to high insurance claims. The state’s coastal properties are particularly vulnerable, contributing to higher premiums.
- High Property Values: Florida has high property values, particularly in coastal areas. Rebuilding or repairing homes in these areas is costly, further increasing insurance rates.
Colorado: $4,099 annually
- Wildfire Risk: Colorado experiences frequent wildfires, which have been increasing in severity due to climate change. These fires can cause significant property damage and loss, driving up insurance costs.
- Hailstorms and Severe Weather: Colorado is also prone to severe weather, including hailstorms, which can cause extensive property damage. This further contributes to higher insurance premiums.
Lowest Home Insurance Rates
Hawaii: $613 annually
- Mild Weather Conditions: Despite the risk of hurricanes, Hawaii experiences relatively few severe weather events compared to mainland states. The state’s tropical climate leads to fewer incidents of extreme weather like tornadoes or hailstorms, which keeps insurance rates lower.
- Stringent Building Codes: Hawaii has strict building codes designed to withstand hurricanes and other natural disasters. These codes reduce the risk of severe damage, thus lowering insurance costs.
New Hampshire: $1,221 annually
- Low Frequency of Natural Disasters: New Hampshire experiences fewer natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires. The reduced risk of such events contributes to lower home insurance premiums.
- Stable Climate: The state’s stable climate with fewer extreme weather variations helps keep insurance rates low. New Hampshire’s geographical location protects it from many of the natural disasters that affect other parts of the country.
Vermont: $1,263 annually
- Low Risk of Natural Disasters: Vermont is less prone to natural disasters compared to other states. The infrequent occurrence of hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires means lower risk for insurers and, consequently, lower premiums.
- Rural Nature and Smaller Homes: Vermont’s rural nature and generally smaller homes mean lower replacement costs, which help keep insurance premiums down.
Washington, D.C.: $1,342 annually
- Moderate Climate: Washington, D.C. has a moderate climate with fewer extreme weather events. The lower incidence of natural disasters like hurricanes and tornadoes reduces the overall risk for insurers.
- Regulatory Environment: The regulatory environment in Washington, D.C. ensures that insurance rates are kept in check, providing some level of protection for consumers against excessive rate hikes.
Delaware: $1,384 annually
- Low Natural Disaster Risk: Delaware experiences fewer natural disasters compared to other states. The lower risk of events like hurricanes and severe storms contributes to lower home insurance rates.
- Effective State Regulations: Delaware’s insurance regulatory framework effectively controls insurance rate increases, helping to keep premiums affordable for homeowners.
Impact of Claims History
A homeowner’s claims history significantly impacts their home insurance rate. Filing multiple claims can drastically increase premiums. For instance, a homeowner with five claims could pay an average of $4,339 annually compared to $1,925 for someone with no claims.

Understanding the home insurance rate differences across states can help homeowners make informed decisions about where to live and how to manage their insurance costs. While climate and weather risks are major factors, state regulations and economic conditions also play crucial roles in determining these rates. It’s essential for homeowners to stay informed and consider these variables when purchasing or renewing their home insurance policies.
Related posts:
 Decline in Home Prices: Anticipating a Shift in 2024
Decline in Home Prices: Anticipating a Shift in 2024
 Maryland Governor Legislative Agenda: Military Families, Housing, and Public Safety in 2024
Maryland Governor Legislative Agenda: Military Families, Housing, and Public Safety in 2024
 Nashville’s Zoning Bills for Middle-Income Housing Spark Contentious Debate
Nashville’s Zoning Bills for Middle-Income Housing Spark Contentious Debate
 Tampa Affordable Housing Initiative Breaks Ground on New 188-Unit Building
Tampa Affordable Housing Initiative Breaks Ground on New 188-Unit Building
 Navigating the Decline: Florida Condo Prices Dropping Amidst Rising Costs
Navigating the Decline: Florida Condo Prices Dropping Amidst Rising Costs