Property tax is a significant consideration for homeowners across the United States, as it varies widely depending on the state and locality. In this 2024 guide, we delve into the intricacies of property tax by state, highlighting the key factors influencing these taxes and offering insights into the states with the highest and lowest rates. Understanding property taxes is crucial for homeowners and prospective buyers alike, as it directly impacts the overall cost of owning a home.

2024 Property Tax Rates by State
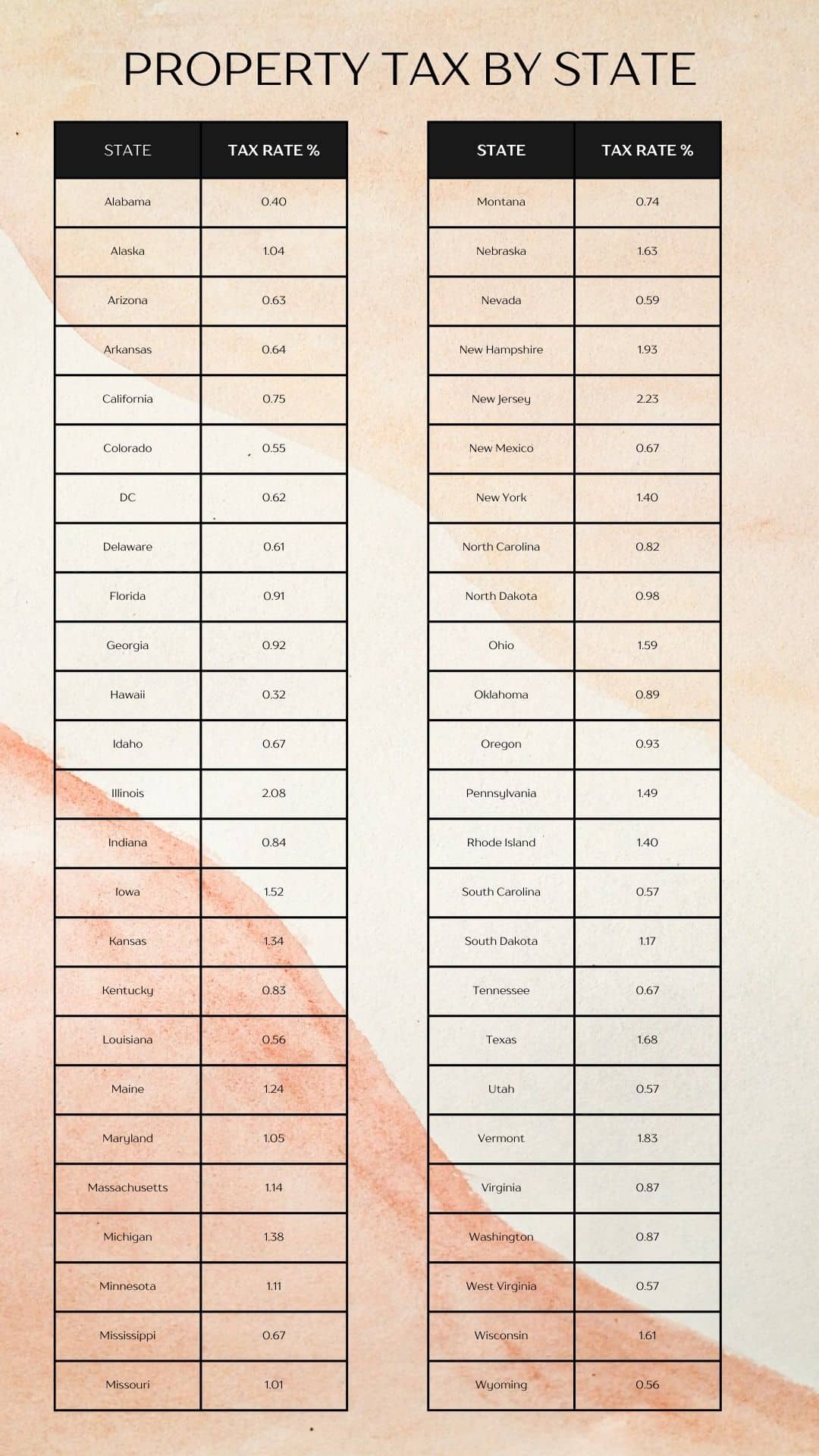
In 2024, property tax by state continues to show significant disparities across the country. States like New Jersey have some of the highest property tax rates, while states like Hawaii offer some of the lowest. Here’s a closer look at the extremes:
- New Jersey: With an effective tax rate of 2.23%, New Jersey has the highest property taxes in the country. Homeowners here pay a median property tax of nearly $9,000 annually.
- Hawaii: On the opposite end, Hawaii boasts the lowest property tax rate at 0.32%. Despite the state’s high property values, the typical tax bill is around $2,000.
Other states with notably high property taxes include Illinois, New York, and Connecticut, each with rates above 1.4%. Conversely, states like Alabama, Arkansas, and Louisiana offer some of the lowest rates, all below 0.65%.
Factors Affecting Property Taxes
Several factors can influence property taxes, leading to variations even within the same state:
- Local Government Spending: Higher spending on local services can lead to increased tax rates.
- Property Values: Rising property values typically result in higher tax bills, while declining values can reduce taxes.
- Tax Laws and Policies: State and local regulations significantly impact how taxes are assessed, the available exemptions, and how taxes can be deferred.
What is Property Tax?
Property tax, often referred to as ad valorem tax, is a tax imposed by local governments based on the assessed value of a property. This tax is a primary source of revenue for local services such as schools, police, and infrastructure. The tax rate is typically expressed as a percentage of the property’s assessed value and can vary significantly from one state to another.
How Property Tax is Calculated
Calculating property tax involves three main components:
- Assessed Value: This is the value assigned to a property by a local tax assessor, based on factors such as recent sales of comparable properties, the income it could generate, or its replacement cost minus depreciation.
- Mill Levy (Tax Rate): The mill levy is the rate at which property taxes are charged, determined by local governments to meet budgetary needs. The rate is applied to the assessed value to calculate the tax owed.
- Exemptions and Deferrals: Homeowners may qualify for various exemptions or deferrals that reduce their taxable value, such as homestead exemptions, senior citizen discounts, or agricultural exemptions.
Managing Your Property Tax Bill
Given the potential burden of property taxes, homeowners should be proactive in managing their tax bills:
- Understand Your Assessment: Review your annual property tax assessment carefully to ensure your home is valued correctly.
- Research Exemptions: Explore available exemptions that could lower your taxable value.
- Appeal If Necessary: If you believe your property is overvalued, you can appeal the assessment with evidence such as comparable sales data or property condition.

Property taxes are a crucial part of homeownership that varies widely across the United States. By understanding the differences in property tax by state and taking steps to manage your tax bill, you can better prepare for the financial responsibilities of owning a home. Whether you’re looking to buy a new home or manage your current property, being informed about property taxes can help you make more strategic decisions.








